对于番茄基因,一加一并不总是等于二
For tomato genes, one plus one doesn't always make two
对于番茄基因,一加一并不总是等于二
by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
通过 冷泉港实验室

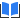
Different combinations of mutations can affect the size of tomatoes unpredictably. In this image, the first column shows an unmutated (WT) tomato. The second and third columns show tomatoes with a single mutation in a region of the promoter (R1 or R4) for fruit size gene SlCV3. The individual mutations have little effect on fruit size. But the combination of these two mutations (R1 + R4) yields a much bigger fruit. Credit: Xingang Wang/Lippman lab, CSHL/2021
突变的不同组合可能会不可预测地影响番茄的大小。在此图像中,第一列显示未突变(WT)的番茄。第二列和第三列显示了在番茄果实大小基因S1CV3的启动子区域(R1或R4)具有单个突变的番茄。单个突变对果实大小影响不大。但是,这两个突变(R1 + R4)的组合产生了更大的果实。图片来源:王新刚/ Lippman实验室,CSHL / 2021
Both people and tomatoes come in different shapes and sizes. That is because every individual has a unique set of genetic variations—mutations—that affect how genes act and function. Added together, millions of small genetic variations make it hard to predict how a particular mutation will impact any individual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator Zach Lippman showed how genetic variations in tomatoes can influence the way a specific mutation affects the plant. He is working toward being able to predict the effects of mutations on different tomato varieties.
人和西红柿都有不同的形状和大小。这是因为每个人都有一组独特的遗传变异(突变),它们会影响基因的行为和功能。数以百万计的微小遗传变异加在一起使得难以预测特定突变将如何影响任何个体。冷泉港实验室(CSHL)教授和霍华德·休斯医学研究所研究员Zach Lippman展示了西红柿的遗传变异如何影响特定突变影响植物的方式。他正在努力能够预测突变对不同番茄品种的影响。
In this study, Lippman and his team used CRISPR, a highly accurate and targeted gene-editing tool, on two tomato genes that control fruit size, SlCV3 and SlWUS. They generated over 60 tomato mutants by removing little pieces of DNA in the promoter regions, areas near the genes that control their expression. In some cases, individual mutations increased the size of the tomatoes by a little bit. Some pairs of mutations did not change fruit size at all. A few synergistic combinations caused a dramatic, unpredicted increase in fruit size. Lippman says:
在这项研究中,利普曼和他的团队使用CRISPR,一种高度精确和有针对性的基因编辑工具,对控制果实大小的两个番茄基因SlCV3和SlWUS进行了研究。他们通过去除启动子区域(靠近控制其表达的基因的区域)的DNA片段,产生了60多个番茄突变体。在某些情况下,个别突变使番茄的大小增加了一点点。有些突变对果实大小没有任何影响。几个协同组合导致了戏剧性的,不可预测的增加水果大小。利普曼说:
"The real Holy Grail in all this for crop breeding is predictability. If I mutate this sequence, I'm going to get this effect. Because there is this sea of other variants that nature has accumulated nearby the mutation that you're engineering, as well as scattered throughout the genome, many of which could be influencing the specific mutation that you're creating."
“对于作物育种而言,真正的圣杯是可预测的。如果我对该序列进行突变,我将获得这种效果。因为在你正在设计的突变附近,自然界中还积聚了其他变种之海,以及散布在整个基因组中,其中许多可能会影响您正在创建的特定突变。”
This range of interactions for any two mutations models the consequences of a single mutation occurring in different genetic backgrounds. The effect is comparable to those found in some human diseases, where some people might have certain pre-existing mutations that protect them from disease-causing mutations.
任何两个突变的相互作用范围都模拟了在不同遗传背景下发生的单个突变的后果。其效果可与某些人类疾病中发现的结果相媲美,在某些人类疾病中,某些人可能具有某些预先存在的突变,可以保护他们免受致病突变的影响。
Lippman and his team will continue quantifying how individual and combined mutations affect certain crop traits. So far, they have measured interactions between two individual mutations, but genomes have millions of variations. Lippman hopes to study enough measurable interactions to make breeding more predictable and efficient.
Lippman和他的团队将继续量化个体突变和组合突变如何影响某些作物性状。到目前为止,他们已经测量了两个个体突变之间的相互作用,但是基因组具有数百万个变异。利普曼希望研究足够的可测量的相互作用,以使繁殖更可预测和更有效。
The study is published in Nature Plants.
该研究发表在《自然植物》上。
点击查看:使用文档翻译功能
免责声明:福昕翻译只充当翻译功能,此文内容及相关信息仅为传递更多信息之目的,仅代表作者个人观点,与本网站无关,版权归原始网站所有。仅供读者参考,并请自行核实相关内容。若需要浏览原文、下载参考文献等,请自行搜索文中提到的原文网站进行阅读。
来源于:phys



 证件证明翻译
证件证明翻译
 医疗病历翻译
医疗病历翻译
 法律合同翻译
法律合同翻译
 公司介绍翻译
公司介绍翻译
 学术论文翻译
学术论文翻译
 留学移民翻译
留学移民翻译
 求职简历翻译
求职简历翻译
 产品说明书翻译
产品说明书翻译